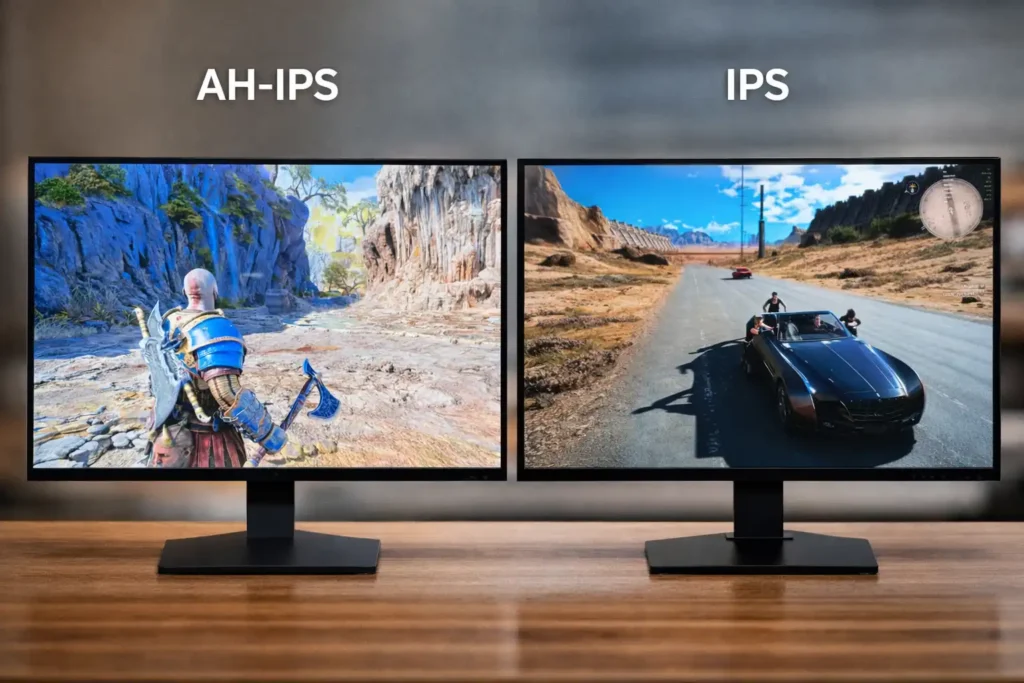
The display panel, also known as the liquid crystal panel, determines most of the number of colors displayed. Along with that, it also affects color accuracy and the speed at which images are refreshed.
Because of this, the role of the display panel is very important and cannot be missing. Choosing the type of panel is just as important.
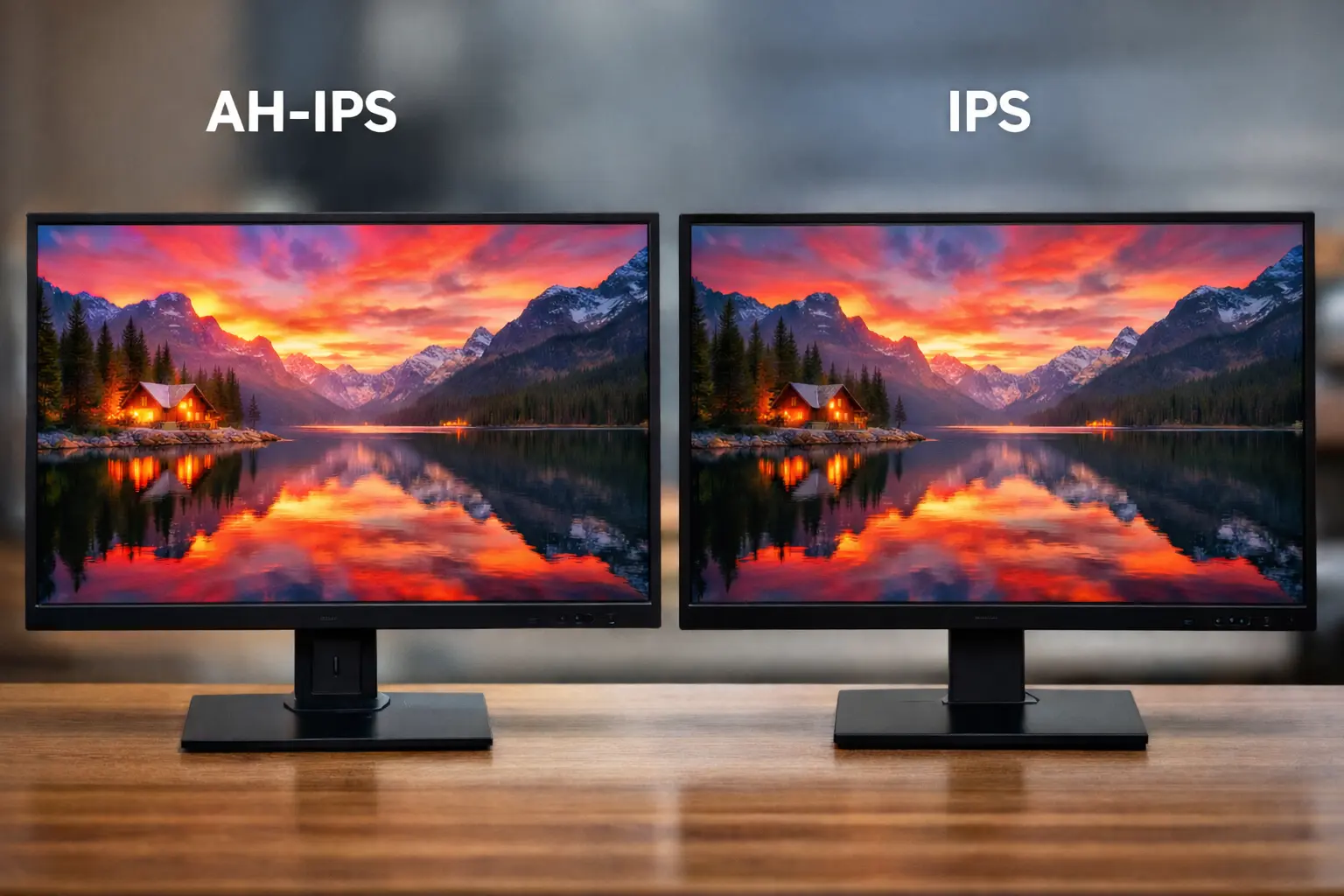

▲ At first glance, AH-IPS and IPS panels appear nearly identical. The difference lies in maximum brightness and efficiency, not in a significantly different image display.
There are two common IPS-based panel types used today: IPS panels and AH-IPS panels.
IPS panels are the older panel type up to this point. Their brightness and efficiency are more limited compared to newer versions.
AH-IPS panels were introduced as a breakthrough, improving on the weaknesses of standard IPS panels. They provide better brightness and more efficient light transmission while keeping wide viewing angles.
| Feature | IPS Panel | AH-IPS Panel |
| Panel type | In-Plane Switching | Advanced High Performance IPS |
| Color accuracy | Good | Very good |
| Viewing angles | Wide (up to 178°) | Wide (up to 178°) |
| Brightness | Standard | Higher |
| Power efficiency | Average | Improved |
| Heat generation | Higher | Slightly lower |
| Typical usage | Mid-range devices | Higher-end devices |
1.Learning about IPS panels
What is an IPS panel?
IPS (In-Plane Switching) is a display technology that is currently one of the most widely used on the market. It is commonly found on devices such as televisions, smartphones, computer monitors, and laptops.
IPS panels were mainly produced to overcome the limitations of older panel technologies. IPS offers more stable image display with wide viewing angles.
Advantages:
IPS panels reproduce images clearly, with accurate colors and wide viewing angles that can reach up to 178 degrees.
When you look at a display with an IPS panel from different angles, the image quality and color accuracy do not change much.
When pressure is applied to the surface of an IPS display, issues such as light bleeding or visible pixel distortion are less likely to occur. This shows that IPS panels are more durable compared to other panel types.
Disadvantages:
IPS panels generate more heat because they use strong backlighting. Because of that, power consumption is higher compared to TN panels.
How to identify an IPS panel:
The most accurate way to identify an IPS display is by checking the viewing angles.
If you look at a screen and change the viewing angle from left to right or from top to bottom, and there is no significant change in sharpness or color, then the display is using an IPS panel.
Devices that use IPS panels:
Currently, IPS display technology is still used on many popular devices such as smartphones, laptops, all-in-one PCs, and desktop monitors.
IPS panels are commonly found in budget and mid-range smartphones from brands such as Vivo, Oppo, and Xiaomi, as well as mid-range laptops from manufacturers like ASUS and Acer.
In addition, IPS technology is also used in all-in-one computers, helping provide better durability, wide viewing angles, and consistent image quality.
Users can sit and work or watch content from almost any angle while still seeing natural and accurate colors.
2. Learning about AH-IPS panels
What is an AH-IPS panel?
AH-IPS (Advanced High Performance In-Plane Switching) is a panel technology that is widely used today. It is an improved version of the standard IPS panel.

AH-IPS was created as a breakthrough to further improve the limitations of IPS panels. AH-IPS provides better brightness and more efficient light transmission while keeping wide viewing angles.
Because of that, AH-IPS panels offer more vivid image display compared to standard IPS panels.
Advantages:
AH-IPS panels reproduce images clearly, with more accurate colors and higher brightness compared to IPS panels.
Viewing angles remain wide, up to 178 degrees, and image quality does not change significantly when viewed from different directions.
AH-IPS panels allow more light to pass through the panel structure. This results in higher brightness levels without increasing power consumption too much.
When looking at the screen from narrow or wide angles, color quality and brightness remain stable.
Disadvantages:
AH-IPS panels generate more heat due to higher brightness output.
Because of their improved structure, AH-IPS panels are more expensive compared to standard IPS panels.
Response time on AH-IPS panels is similar to IPS panels and is slower compared to TN panels.
How to identify an AH-IPS panel:
The most accurate way to identify an AH-IPS panel is by checking the manufacturer’s specifications.
From a visual perspective, AH-IPS and IPS panels look very similar. However, AH-IPS panels usually offer higher brightness.
When changing viewing angles from left to right or from top to bottom, AH-IPS panels maintain stable image quality and color accuracy.
Devices that use AH-IPS panels:
Currently, AH-IPS technology is used on many modern devices, especially higher-end monitors and laptops.
AH-IPS panels are often found in premium displays where higher brightness and better color accuracy are required.
High-resolution monitors frequently use AH-IPS panels to ensure consistent image quality and efficient power usage.
Users can work and view content from any angle while still seeing natural and accurate colors.
3. AH-IPS vs IPS
AH-IPS vs IPS is mainly about brightness and efficiency.
IPS panels provide good color reproduction and wide viewing angles.
AH-IPS panels improve brightness and energy efficiency while keeping the same viewing angle performance.
Both panel types have their own advantages and disadvantages, depending on usage needs.
Summary:
IPS panels provide good image quality and wide viewing angles, but brightness is limited.
AH-IPS panels provide better brightness, improved efficiency, and more vivid image quality.
Both IPS and AH-IPS panels offer stable colors and wide viewing angles suitable for everyday use.
