It is a dynamic contrast ratio feature of modern monitors designed to improve image quality by dynamically adjusting contrast and brightness based on the content being displayed.
As monitors become central to work and entertainment features like DCR can play a significant role in providing a better viewing experience.
This comprehensive guide explores how DCR works, its pros and cons.
Understanding DCR
DCR is a software driven feature that allows monitors to modify contrast levels in real-time based on the visual content being displayed. By dynamically changing the backlight intensity and adjusting gamma settings. DCR enhances both dark and bright areas of the screen. Read our guide What is FHD?

For example during dark movie scenes the monitor reduces the intensity of the backlight to deepen the black color creating a more immersive experience. Read our guide What is HDCR on MSI Monitors?
How Does DCR Work?
DCR operates using real-time content analysis. Here’s how it functions:
- Content Analysis: The monitor evaluates the brightness and contrast levels of the content displayed.
- Backlight Modulation: For darker scenes, the backlight dims to improve black depth; for brighter scenes, it increases brightness to enhance clarity.
- Gamma Adjustments: The gamma curve adjusts dynamically to ensure the displayed content looks as natural and vivid as possible.
This combination of backlight modulation and gamma adjustments creates an optimized visual experience that adapts to varying content.
Key Benefits of DCR
1. Improved Visual Quality
DCR improves the contrast of darker areas without making bright areas overly intense. This is especially noticeable when watching movies or playing games. For example, in movies, DCR helps bring out shadow detail in darker scenes, while ensuring that highlights, like a dazzling sunset or a bright explosion, remain sharp and vivid.

This balanced setup allows viewers to enjoy a more realistic and immersive image without having to manually adjust monitor settings.
2. Enhanced Immersion
By deepening blacks and brightening whites, DCR makes scenes appear more lifelike. This can significantly enhance immersion in gaming or cinematic experiences. For instance, in narrative-driven video games with complex lighting environments, DCR brings depth to nighttime sequences while emphasizing the brilliance of magical effects or explosions. Read our guide LG vs. Samsung Monitors.
Similarly, cinematic movies shot in high contrast, such as thrillers or space adventures, feel more engaging as DCR amplifies the visual drama.
Moreover, this level of immersion can create a more emotional connection with the content, pulling viewers or players deeper into the story or action unfolding on the screen.
3. Adaptability to Different Content
DCR automatically adjusts based on what’s displayed, offering flexibility for diverse content like movies, games, and photos. This adaptability means you don’t need to constantly switch monitor settings manually when transitioning from one activity to another. Watching a movie? DCR ensures darker scenes are rich in detail. Playing a game?
DCR makes the environment pop with lifelike visuals. Editing photos? DCR ensures accurate contrasts to highlight textures and fine details. Read our guide What is ASCR?.
This versatility is especially useful for users who multitask or share a monitor for both work and leisure, as it seamlessly transitions to suit varied needs without compromising quality.
4. Better in Low Light
DCR excels in dimly lit environments, making it easier on the eyes and providing a more cinematic feel. For example, when watching a movie in a dark room, DCR minimizes the harshness of bright scenes, reducing eye strain. It also enhances the subtleties of shadowy areas, giving scenes a dramatic, theater-like effect. WQHD offers a significant upgrade in clarity over FHD, making it a popular choice for gamers and professionals. Read more about it in our article on What is WQHD Resolution?.

This capability is particularly useful for gamers who often play in low-light setups, as it prevents glare while maintaining visual clarity. Additionally, DCR’s ability to reduce overly bright flashes can help mitigate fatigue during long viewing or gaming sessions. This makes it a preferred choice for late-night binge-watchers and dedicated gamers alike. Read our guide 1500R vs 1800R Curved Monitor.
DCR for Gaming: Is It Worth It?
Advantages for Gamers
DCR enhances visibility in games by dynamically adjusting contrast, especially in titles where dark environments or bright highlights are critical. For instance:
- In FPS games, DCR helps you see enemies hiding in shadows.
- In open-world games, it enriches the vibrancy of colorful landscapes and enhances the drama of night scenes.
Drawbacks for Gamers
However, DCR may not be suitable for competitive or fast-paced gaming:
- Input Lag: The dynamic adjustments might introduce slight delays, which can affect reaction times in fast-action scenarios.
- Distractions: The shifting contrast may feel unnatural or distracting, particularly in games with rapidly changing scenes.
For gamers, it’s worth experimenting with both enabled and disabled DCR settings to find the balance that works best for their needs.
DCR vs. ACR: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | DCR (Dynamic Contrast Ratio) | ACR (Advanced Contrast Ratio) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software-based real-time contrast adjustment | Proprietary enhanced contrast technology |
| Focus | Enhances contrast based on content | Focuses on deeper, refined contrast levels |
| Usage | Commonly used for multimedia and gaming | Typically found in specific monitor models |
| Customization | Limited user control | Often includes more granular settings |
While DCR is widely used, ACR is typically proprietary to certain brands, offering advanced algorithms for improved results.
Technical Details: How DCR Achieves Dynamic Contrast
Backlight Modulation
The monitor’s backlight is adjusted in real-time:
- In Bright Scenes: The backlight is increased to enhance clarity.
- In Dark Scenes: The backlight is dimmed to provide deeper blacks.
Dynamic Gamma Adjustment
Gamma correction fine-tunes the contrast to optimize images for human vision. By dynamically altering gamma curves, DCR ensures a more natural and visually pleasing result.
Applications of DCR
1. Watching Movies
DCR shines when you’re watching high contrast content like action movies. It enhances shadow detail while ensuring that bright areas don’t get washed out.

For example in action packed sequences, explosions and fire appear more vivid, while dark corners or shadowed areas reveal hidden details that might otherwise go unnoticed. This level of dynamic adjustment creates a cinematic effect, allowing you to experience movies the way the filmmakers intended.
2. Gaming
As discussed earlier, DCR provides more dramatic and immersive visuals for gaming, making it ideal for single-player or story-driven games. Games with expansive worlds, like RPGs or adventure titles, benefit from DCR’s ability to bring out the richness in environmental details, from the glow of a setting sun to the shadows of dense forests. In darker levels or dungeons, DCR ensures you don’t miss critical details, like hidden paths or lurking enemies.

Additionally, gamers who enjoy cinematic cutscenes will appreciate how DCR brings a polished, professional quality to in-game storytelling. While competitive gamers might prioritize speed over visuals, casual or narrative-focused players will find DCR enhances their overall enjoyment.
3. Everyday Use
For browsing, streaming, or editing photos, DCR adds vibrancy and depth, ensuring content looks its best without manual adjustments. Websites with vivid images, videos on streaming platforms, and even social media feeds benefit from improved contrast and color depth.

Photo editors and hobbyists will appreciate how DCR subtly enhances details in pictures, making shadows richer and colors more pronounced.
This is particularly helpful when sharing visuals online, as the enhanced contrast can make an ordinary image look more professional. For casual users, the seamless adaptability of DCR ensures a better visual experience across all tasks without needing to tweak settings constantly.
Limitations of DCR
Despite its advantages, DCR has some limitations:
- Artifacts: Poorly implemented DCR can cause halos or blurring in high-contrast scenes.
- Inconsistent Results: Not all content benefits equally, especially static displays like spreadsheets or text documents.
- Potential Distractiveness: The dynamic changes in brightness may feel unnatural for some users.
Alternatives to DCR
1. HDR (High Dynamic Range)
HDR improves both contrast and color, creating a wider dynamic range and richer images.
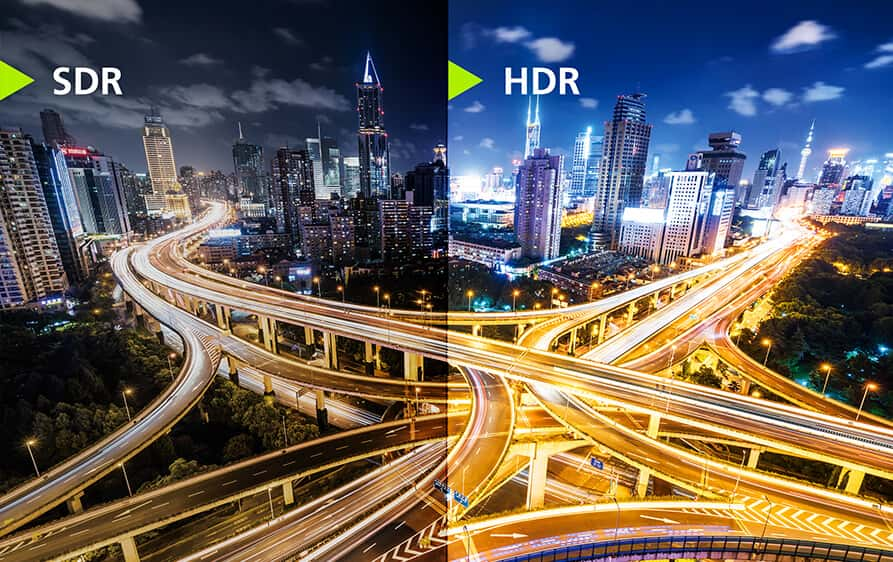

Unlike DCR, which focuses primarily on contrast adjustment, HDR extends the monitor’s ability to display a wider range of brightness levels and more vivid colors.
2. Local Dimming
Local dimming divides the backlight into zones, adjusting each zone independently for better contrast and less glare.

This technology allows the display to illuminate certain parts of the screen while keeping others dark, effectively creating a higher contrast ratio than traditional backlighting methods.
3. Quantum Dot Technology
Quantum dots are microscopic particles that emit very pure and vivid colors when exposed to light. This technology is used in modern displays to significantly improve color accuracy and brightness.

By incorporating quantum dots into LCD panels, manufacturers can achieve a much wider color gamut and deeper contrast than traditional LCD displays.
DCR vs. Static Contrast Ratio
| Aspect | Static Contrast Ratio | Dynamic Contrast Ratio (DCR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed ratio of brightest white to darkest black | Variable ratio based on displayed content |
| Customization | None; hardware-dependent | Adjusts dynamically via software |
| Performance | Consistent | Adaptive, optimized for specific scenes |
Static contrast ratios are hardware-based, while DCR adds adaptability to enhance visual performance dynamically.
Conclusion
Dynamic contrast ratio is a valuable feature for improving monitor performance by dynamically adjusting contrast and brightness.

DCR can enhance your experience with richer visuals and deeper blacks.
While not perfect for every scenario, DCR is a significant step forward in making monitors more responsive and visually appealing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should I enable DCR on my monitor?
If you watch movies, game, or work with multimedia content, DCR can improve visuals. However, for static content like text, it may not add significant value.
Is DCR good for competitive gaming?
For competitive gaming, DCR’s input lag might be a drawback. Casual gamers, however, may appreciate its enhancements.
Can DCR damage my monitor?
No, DCR is a software feature that doesn’t physically affect your monitor’s components.
How is DCR different from HDR?
DCR focuses on contrast adjustments, while HDR enhances both color and contrast for a broader dynamic range.
What is Advanced DCR?
Advanced DCR is an enhanced version of DCR, offering refined algorithms and improved contrast adjustments for better image quality.
References
- https://www.mobilepixels.us/pages/what-is-dcr-on-a-monitor#:~:text=Dynamic%20Contrast%20Ratio%20(DCR)%20is,bright%20colors%20on%20the%20screen
- https://rehisk.com/blogs/blogs/what-is-a-dcr-monitor-complete-guide?srsltid=AfmBOorgQewbxa8vpvdqz1w6VtwGwbZjNazoEPXd7pIb_MahgdcCNPSc
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DCR#:~:text=Dynamic%20contrast%20ratio%2C%20referring%20to,property%20of%20a%20display%20system